Ultimate Guide to Instructional Design: Everything You Need to Know
Nov 08, 2023
Table of Contents:
Introduction to Instructional Design
What is Instructional Design?

Instructional Design is a systematic and iterative process that revolves around the development of well-designed and engaging learning experiences and environments. Its aim is to create highly effective instructional models that enhance learning outcomes by aligning with the unique needs and preferences of learners, while also bridging the knowledge gap.
This discipline goes beyond the mere delivery of information. It focuses on creating meaningful and interactive learning experiences that promote knowledge retention and application. By analyzing learners' needs, understanding their learning styles and preferences, and designing instructional strategies and materials that cater to these individual requirements, instructional design ensures a tailored approach to education.
Incorporating principles from various fields such as cognitive psychology, educational technology, and human-computer interaction, instructional design makes learning more efficient, effective, and less complicated. It emphasizes the use of multimedia, interactive activities, and assessments to facilitate active learning and ensure learner engagement throughout the instructional process.
Ultimately, instructional design has the power to transform traditional teaching and learning approaches into dynamic and learner-centered experiences. By leveraging innovative instructional techniques and technologies, instructional designers strive to create courses that not only meet learning objectives but also inspire and empower learners to become active participants in their own educational journey.
If you're new to the industry, are pivoting from another field into the world of ID, or just want to take your instructional design talents to the next level, you've found the right place. IDOL Courses will not only provide you with an instructional design certificate from the first and only state-authorized vocational school for instructional design and online learning, but it will provide you with the tools, resources, and talent you'll need to land your next IDOL role.
Importance and Impact of Instructional Design in Various Industries

Instructional design's impact is far-reaching, influencing various industries and sectors beyond the realm of formal education. In the business world, it plays a critical role in employee training and professional development. Organizations utilize instructional design strategies to create training programs that enhance employees' skills and knowledge, leading to improved performance and productivity. Moreover, these programs facilitate new employee onboarding, ensuring they quickly grasp their roles and responsibilities. Instructional design is also employed to develop customer education programs, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.

The healthcare industry also extensively utilizes instructional design to train medical professionals in complex procedures and protocols, ensuring patient safety and care quality. It aids in the creation of simulation-based training, which allows healthcare professionals to practice in a risk-free environment before real-life application. In the technology industry, instructional design aids in software and application training, ensuring efficient user experience and reducing the learning curve. Similarly, in the non-profit sector, it assists in creating effective volunteer training programs, ensuring individuals are equipped with the necessary skills to perform their duties. Hence, instructional design's impact is diverse and transformative across various industries, which means obtaining your instructional design certificate will give you a competitive edge in an industry with so many possibilities.

In vocational schools, instructional design has heralded significant changes and improvements in the delivery of education. These institutions, which focus on providing students with specific trade skills, greatly benefit from instructional design's systematic approach to teaching and learning. The incorporation of interactive materials, multimedia, and assessments tailored to the practical nature of vocational subjects increases student engagement and understanding of their chosen trade. With instructional design, vocational schools can create simulations and virtual environments where students can practice skills in a controlled, risk-free setting before applying them in real-world situations. Ultimately, instructional design enables vocational schools to offer a more personalized, efficient, and effective approach to skills-based learning, improving student outcomes and enhancing their readiness for the workforce.
Career Prospects in Instructional Design

The field of instructional design offers diverse and rewarding career opportunities. As an instructional designer, one can work in various sectors such as academia, corporate, government, non-profit organizations, healthcare, and technology. These professionals are responsible for designing, developing, and implementing effective instructional materials and learning experiences. They work closely with subject matter experts, incorporate instructional theory and best practices into their designs, and use emerging technologies to enhance learning outcomes.
The rapid digitalization of education and the increased use of e-learning platforms have further expanded job prospects for instructional designers. Roles such as e-Learning Developer, Learning Experience Designer, and Educational Technologist are becoming more prevalent, focusing on the creation of interactive digital learning experiences and courses. Additionally, some instructional designers choose to specialize in areas like mobile learning, gamification, or learning analytics, adding another layer of depth to their career options. Salary prospects in this field are promising, with the median annual wage for instructional designers and technologists significantly higher than the national average for all occupations. Whether you're a creative thinker, problem-solver, or tech-enthusiast, the field of instructional design offers a dynamic and fulfilling career path.
Key Principles of Instructional Design
The Addie Model of Instructional Design
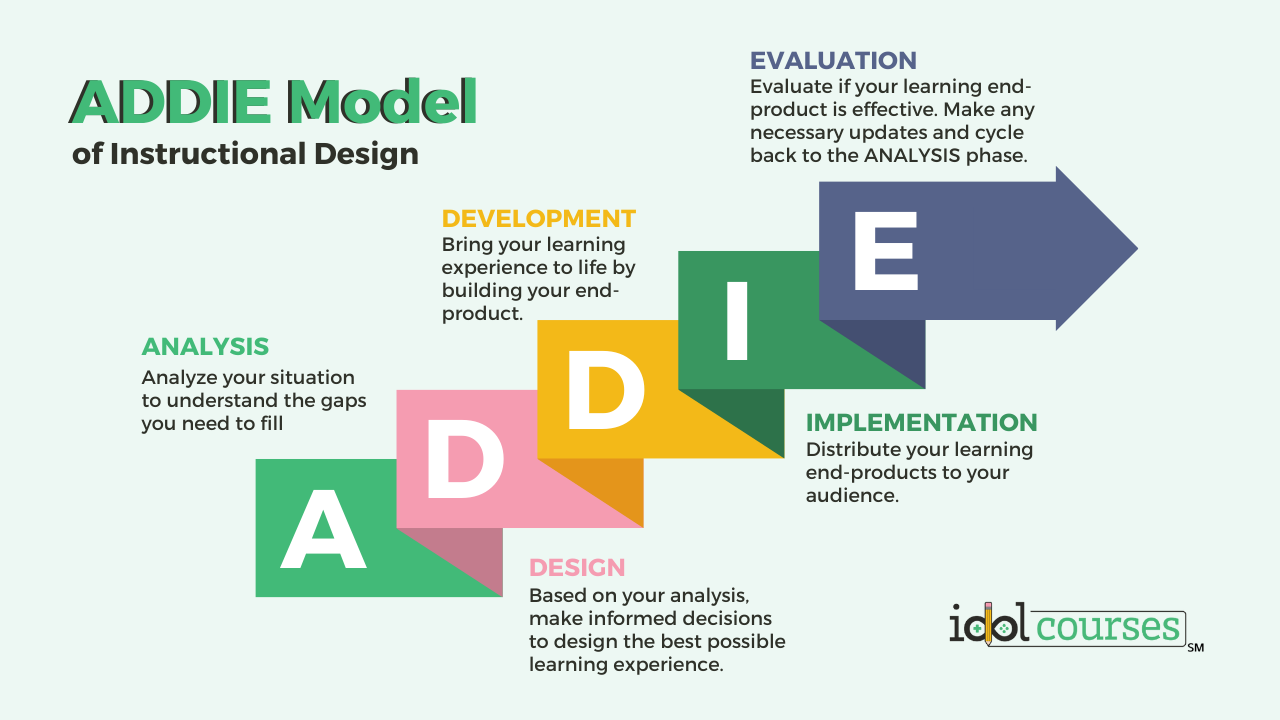
The ADDIE model is a systematic instructional design model consisting of five phases: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. Each phase has a specific purpose and is a vital part of the overall process.
- Analysis: In this stage, instructional designers identify the learning needs of the target audience, define clear learning objectives, and understand the environment in which learning will take place.
- Design: In this phase, instructional designers plan the instructional strategy, define the content, and decide on the tools and methods to be used for delivering the instruction.
- Development: This stage involves the creation of the actual learning materials. It may include scripting, storyboarding, content development, and testing of the learning materials.
- Implementation: During this phase, the instructional materials are delivered or distributed to the learners. This could be in a classroom setting, online, or through a blended approach.
- Evaluation: The final stage involves assessing the effectiveness of the instructional materials. This could be through feedback from learners, assessments, or observing behavioural changes in the learners.
The ADDIE model is iterative, meaning that feedback from each phase can lead to modifications in the previous stages, ensuring continuous improvement and high-quality instruction.
Effective Instructional Design Strategies and Methodologies
“We've heard that content is king, but even more specifically, when you get a full demonstration of a real-world context and you are put into a situation where you are solving the problems yourself, and you are immersed in the learning, the motivation comes from building mastery.” --Dr. Robin Sargent, IDOL Courses Chief Learning Officer
Several effective instructional design strategies and methodologies are key to successful learning outcomes. First, the Problem-Based Learning (PBL) method encourages learners to acquire knowledge and skills by solving realistic, complex problems. Second, the Multimedia Principle suggests using both words and visuals for instruction to enhance understanding. Third, Microlearning allows for chunking information into small, manageable units, improving comprehension and retention. Fourth, the Gamification technique uses game elements in non-gaming contexts, making learning interactive and engaging. Lastly, Blended Learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, providing flexibility and convenience while maintaining personal contact and collaboration. These diverse strategies cater to different learning styles, fostering an inclusive and effective learning environment.
Incorporating Adult Learning Principles
Incorporating adult learning principles into instructional design is key to creating effective learning experiences for adult learners. One of the most widely recognized theories in adult learning is Malcolm Knowles' Andragogy, which asserts that adults are self-directed, possess a wealth of experience, are ready to learn, and prefer learning that is relevant and problem-centered.
Instructional design can leverage these principles by creating learning experiences that are learner-centered and practical. For instance, instructional materials can be designed to allow learners to draw from their professional and personal experiences, facilitating peer learning and sharing. This not only enhances the relevance of the learning experience but also promotes critical thinking and reflective learning.
Furthermore, adult learners prefer to be involved in their learning journey. Hence, an effective instructional design should provide opportunities for self-directed learning—where learners can set their own learning goals, manage their learning process, and evaluate their progress. This can be facilitated through e-learning platforms that offer flexible pacing, interactive learning modules, and real-time feedback. By aligning with adult learning principles, instructional design can better engage adult learners, improve their learning experience, and enhance learning outcomes.
Tools and Technologies in Instructional Design

Popular Instructional Design Software and Tools
The industry of instructional design is abundantly equipped with cutting-edge software and tools that significantly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of the design process. Among the leading technologies, Articulate Storyline and Adobe Captivate stand out for their comprehensive features enabling designers to create interactive and engaging e-learning courses. TechSmith Camtasia is another powerful tool designed for creating professional-grade videos and tutorials with ease. For collaborative efforts, tools like Google Workspace facilitate real-time collaboration on design projects, while project management tools like Trello and Asana help keep the design process organized and on track. Furthermore, Learning Management Systems (LMS) such as Workday, Moodle, Cornerstone, and Canvas offer platforms to deliver, track, and manage the learning process effectively. In the realm of instructional design, online learning platforms play a pivotal role. They serve as the digital hubs where instructional materials are delivered, accessed, and interacted with by learners. By harnessing the power of these tools, instructional designers can create high-quality, engaging, and impactful learning experiences.
Online Learning Platforms

There are a plethora of online learning platforms that command popularity due to their diverse course offerings and interactive learning environments. As an instructional designer, you can augment your company's learning materiels with already curated courses from these resources. Coursera and edX, for instance, partner with universities and institutions worldwide to offer courses across various disciplines, including data science, business, and humanities. Udemy stands out with its vast array of courses covering fields from software development to music, each designed and instructed by experts in the area. LinkedIn Learning offers an extensive library of courses tailored towards professional development across various industries. Lastly, Khan Academy is a unique non-profit platform that offers free, high-quality education to anyone, anywhere, with a strong focus on foundational knowledge in math, science, and arts. Each platform shapes the e-learning landscape in unique way
Multimedia and visual design tools for engaging content creation
The creation of engaging e-learning content for adult learners significantly benefits from the use of multimedia and visual design tools. Tools such as Canva and Adobe Creative Suite offer a range of features for creating visually appealing content, from infographics to interactive elements. They enable designers to incorporate images, videos, animations, and other multimedia forms into their learning resources, transforming static content into dynamic, engaging learning experiences. Powtoon and Vyond are popular for creating animated videos, known for their effectiveness in capturing attention and explaining complex ideas in digestible ways. Additionally, data visualization tools like Tableau are useful for representing data or information in a visually intuitive manner, promoting better understanding and retention. Using these tools, instructional designers can create content that appeals to adult learners' visual sense, thereby enhancing engagement and learning outcomes.
Instructional Design Process and Workflow
The instructional design process follows a systematic approach to ensure effective and efficient learning.
- Needs Analysis: This initial step involves identifying and analyzing the learning needs of the target audience. The aim is to understand what the learners already know and what they need to learn, their learning styles, and any potential barriers to learning.
- Learning Objectives: Once the needs are identified, the instructional designer sets clear, measurable learning objectives. These objectives outline what the learners should be able to do at the end of the course.
- Content Creation: The designer develops course content and materials that align with the learning objectives. This involves structuring the content in a logical sequence, selecting appropriate instructional strategies, and incorporating relevant multimedia to enhance engagement.
- Instructional Strategy Development: The designer decides on the best methods to deliver the content. This may involve lectures, interactive activities, group discussions, or a blend of multiple teaching strategies.
- Development of Assessment Tools: The designer creates assessments to measure learner's understanding and application of the knowledge gained. These assessments should align with the learning objectives.
- Implementation: The course is now ready to be delivered to the learners. The designer facilitates the course, ensuring the learning environment is conducive and the course content is delivered as planned.
- Evaluation: The final step involves evaluating the effectiveness of the course. Feedback from learners is gathered, and the course materials are reviewed for any necessary revisions or improvements.
This process is a cycle, and the designer may return to any step as needed based on the evaluation and feedback.
Collaboration with Subject Matter Experts and Project Management in Instructional Design

SMEs
Effective instructional design is often a result of a collaborative effort between instructional designers and Subject Matter Experts (SMEs). SMEs bring the necessary depth of knowledge in a particular area, while instructional designers apply their expertise in creating engaging and effective learning experiences. This synergy is achieved through regular communication, understanding each other's perspectives, and leveraging each other's strengths. Tools such as Trello, Slack, and Microsoft Teams can facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between the two parties. What's most important to note is that you, the Instructional Designer, must be the guide throughout the whole process.
Nicole Papaioannou Lugara of Your Instructional Designer tells us, "As the SME provides expertise on the subject, the ID transforms it into learning experiences. This may include digital courses, instructor led training (ILT), virtual instructor-led training (vILT), social learning, game based learning, structured on the job training (OJT), blended learning, or other solutions that are context appropriate.
The most important thing for you to remember: creating learning products is a collaborative process that requires many conversations and formal feedback cycles."
Project Management in Instructional Design
In managing multiple projects with competing deadlines, instructional designers employ project management principles and techniques. Prioritization is crucial, which involves assessing the urgency and importance of various tasks and allocating resources accordingly. Instructional designers also use project management tools such as Asana, Basecamp, or Monday.com to track progress, assign tasks, set deadlines, and manage workflows. These platforms provide a visual overview of all the projects, facilitating efficient management and timely completion.
Moreover, instructional designers often use agile methodologies for managing multiple projects. This approach involves breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable parts, followed by iterative cycles of development. This allows for adjustments and refinements based on feedback, leading to a better end product while also maintaining momentum towards project completion. Agile methodologies provide flexibility, which is particularly beneficial when managing multiple projects with differing scopes and deadlines.
Meaningful and Effective Assessments in Instructional Design

Designing meaningful and effective assessments in instructional design is a multi-step process. It begins with aligning assessments with the established learning objectives. Each assessment should measure a learner's ability to meet a specific learning objective, ensuring a direct correlation between what is taught and what is evaluated.
The next step is to choose the appropriate assessment type based on the learning objective. For factual knowledge, multiple-choice or fill-in-the-blank questions might be sufficient. However, for more complex objectives involving problem-solving or critical thinking, case studies, essays or projects may be more suitable.
The design of the assessment should also consider the learners' context and apply real-world scenarios wherever possible. This rendering of practical context not only makes the assessment more relevant but it also enables learners to apply the concepts and skills they've learned in a realistic scenario.
Feedback is another crucial component in assessment design. Immediate, specific, and constructive feedback helps learners understand their strengths and areas for improvement. It also guides them in the right direction for continuous learning and improvement.
Finally, assessments should be fair and unbiased. The questions should be clear, unambiguous, and designed in a way that all learners, regardless of their backgrounds, have an equal opportunity to demonstrate their understanding and knowledge. This might involve considering factors such as cultural sensitivity and accessibility for learners with disabilities.
In summary, meaningful and effective assessments in instructional design are those that are aligned with learning objectives, contextually relevant, provide constructive feedback, and promote fairness and equality.
Trends and Innovations in Instructional Design

Emerging Technologies
As instructional design continues to evolve, emerging technologies are playing an increasingly important role in shaping the field.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are two such technologies, offering immersive experiences that make learning more engaging. VR and AR can simulate real-world scenarios, enabling learners to practice skills in a safe and controlled environment.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also reshaping instructional design. AI can personalize learning experiences, adapt content to each learner's needs, and provide real-time feedback. It also has the potential to automate certain tasks, such as grading and data analysis, freeing up time for instructional designers to focus on more complex aspects of course design.
Learning Analytics use data collection and analysis to improve learning experiences and outcomes. By tracking learners' behaviors and performances, instructional designers can gain insights into what works and what doesn't, allowing for continual refinement of the instructional design process.
Gamification Tools for Instructional Design
One of the more innovative tools used to enhance instructional design is Genially, a versatile online platform that supports the creation of interactive and engaging content through gamification. Genially allows instructional designers to create interactive presentations, infographics, quizzes, escape games, and even interactive images. These tools can provide a game-like learning experience, increasing student participation and motivation. The platform offers a user-friendly interface, a wide variety of templates, and the opportunity to incorporate a range of multimedia elements, making the learning experience entertaining as well as educational. The use of Genially, and gamification tools alike, is testament to the evolving field of instructional design, which continually adopts creative strategies to enhance the learning experience.
Articulate 360 and Lectora are prominent tools in e-learning that can be leveraged for gamification to enhance learner engagement and motivation. Articulate 360 comes with a suite of software, including Storyline 360 and Rise 360. Storyline 360 allows instructional designers to create custom, interactive games through its powerful and flexible features. Designers can utilize triggers, variables, and layers to design intricate game mechanics, such as scoring systems, progress tracking, or interactive game scenarios. Rise 360, on the other hand, is ideal for designers who prefer a more streamlined, template-driven approach to gamified content creation. It offers interactive block templates that can quickly be turned into games or quizzes, providing an engaging learning experience.
Lectora, renowned for its robust capabilities and flexibility, is another powerful tool for gamification. It allows the creation of gamified elements such as quizzes, puzzles, and simulations using variables, actions, and conditions. It also supports integration with tools like BranchTrack for creating complex branching scenarios and games. Furthermore, Lectora's responsive design ensures that the gamified learning experience is accessible and enjoyable across all device types. Both Articulate 360 and Lectora provide instructional designers with the tools to transform traditional course content into dynamic, interactive, and engaging learning experiences, demonstrating the potential of gamification in e-learning.
Microlearning and Mobile Learning Trends in Instructional Design
Microlearning and mobile learning are taking the world of instructional design by storm, transforming the way learners interact with educational content.
Microlearning is a trend focused on delivering content in small, manageable units. This approach aligns with the modern learner's preferences for concise, targeted learning experiences that can be absorbed in short time spans. Microlearning is effective across various platforms, from desktops to mobile devices, and fits into learners' busy schedules. An emerging trend in microlearning includes "learning in the flow of work", where educational content is integrated into daily tasks, allowing learners to apply new knowledge or skills immediately.
Furthermore, interactive video-based learning is gaining traction in the microlearning sphere. These videos incorporate quizzes, scenarios, and simulations to engage learners actively, improving information retention and application.
Mobile learning, or mLearning, optimizes educational content for handheld devices. This approach supports learning on-the-go, fitting education into the pockets of learners. The primary trend in mobile learning is the development of mobile apps for learning. These apps offer interactive and personalized learning experiences tailored to the learner's pace and preferences. Mobile Learning capitalizes on the ubiquity of smartphones and tablets, enabling learners to access educational content anytime, anywhere. This flexibility can enhance learner engagement and facilitate ongoing learning outside of traditional settings.
Stay connected with news and updates!
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
Don't worry, your information will not be shared.
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.


